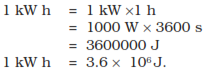All living beings need food, living beings must perform several basic
activities to survive. We call such activities as life processes.
The energy for these processes comes from food, we need energy for doing
other activities like playing, singing, reading, writing, thinking, jumping
activity and it is more strainers then we require more energy. Similarly,
machines come across the same need. For the functioning of a machine their
need fuel like petrol, diesel or electricity which can give energy to the
machine for their functioning,
Work
Work done by an object is defined as the magnitude of the force applied
multiplied by the distance moved by the object in the direction of the
applied force. The unit of force is joule. 1 joule can be defined as one
Newton of force multiplied by 1 metre displaced by the force.
If we push a heavy rock for a long time but there is no displacement of the
rock, though we wasted a lot of energy in doing so but work done is said to
be zero. This is because there is no movement in the position of the rock,
if we go by the scientific definition of work done.
Again if we run on a circular track, starting from a particular. Then comes
to end after reaching that same point. Then total work done is said to be
zero because there is no displacement of our body.
Scientific conception of work
For a work is said to be done two conditions are needed to be satisfied:
A force should act on an object.
The object must be displaced.
When we push a pebble lying on a surface the pebble moves through a
distance. This is because the force exerted on the pebble and that resulted
in the pebble getting displaced.
We can lift a book through a particular height by applying force. Force
applied to lift the book to a certain height and hence we consider work is
done.
Work done by a constant force
When we consider a case where the force is acting in the direction of
displacement. We considered a constant force f applied on an object that
moves through a distance of s in the direction of force, then the work done
is equal to the product of the force and displacement.
W= fs
Work done is said to be negative when the force acts opposite to the
direction of displacement, it is only positive when the force is in the
direction of displacement.
Energy
The capability of doing a work is said to be the energy of a particular
object. Without energy life is impossible, the demand for energy is ever
increasing. The prime natural source of energy is the sun. We can also get
energy from nuclei of atom, the interior of earth, and the tides.
While performing some work the object which does the work loses energy and
the object on which the work is done gains energy.
The unit of energy is therefore the same as that of work that is joule. 1
joule of energy is required to do one joule of work. Sometimes a larger
unit of energy called kilo joule is used 1 kilo joule is equals to 1000
joule.
Forms of energy
Energy is provided in different forms. The various forms of energy include
potential energy, kinetic energy, heat energy, chemical energy, electrical
energy and light energy.
Kinetic energy
Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. The
kinetic energy of an object increases with its speed.
Kinetic energy of a body moving with a certain velocity is equal to the
work done on it to make it acquire that velocity. A moving bullet, blowing
wind and rotating wheel have some speed involved in it and therefore
possess kinetic energy.
The kinetic energy possessed by an object of mass m and moving with uniform
velocity can be expressed by the following formula.
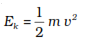
Potential energy
the energy possessed by an object is the energy present in it by virtue of
its position or configuration is called as the potential energy of the
object.
The energy that gets stored due to the work done on the object if it is not
used to cause any change of velocity or speed of the object.
Potential energy of an object at a height
an object increases its energy when raised through a height this is because
the work done on it against gravity while it was being raised to that
position. Search potential energy present in an object is term termed as
gravitational potential energy.
Gravitational potential energy of an object at a point above the ground is
defined as the work done in raising it from the ground to that point
against gravity.
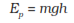
Minimum amount of force required to raise the object is equal to the weight
of the object that is mg. Then the potential energy stored in that object
is mgh, where h is the height of the position of the object.
Energy forms interconvertible
The conversion of energy from one form to another can be seen in many
instances in natural process.
Law of conservation of energy
According to the law of conservation of energy, energy can only be
converted from one form to another it can neither be created nor
destroyed.
The total energy before and after the transformation remains the same. When
we consider an object with mass m freely falling from height h then the
potential energy at the beginning is mgh, when the kinetic energy is zero
when it falls with a velocity v then the potential energy of the object
changes into kinetic energy. As the fall of the object continues the
potential energy decreases and the kinetic energy increases until it
reaches the ground that is h = 0 and velocity v will be highest. So, the
sum of potential energy and kinetic energy during the fall at any point is
constant.
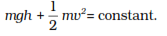
Rate of doing work
power is defined as the rate of doing work or the rate of transfer of
energy. Power measures the speed of work done that is how first or slow
work is done by an agent.
Power of an agent can be determined by the work done divided by the total
time taken to complete the work.
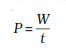
The SI unit of power is watt, that is joule per second. 1 watt of power of
an agent, is when the work done is at a rate of 1 joule per second. 1
kilowatt is equals to 1000 watt.
Commercial unit of energy
The unit joule is too small and hence is inconvenient to express large
quantities of energy. We use a bigger unit of energy called kilowatt hour
(kW h). A machine that uses 1000 J of energy every second. If this machine
is used continuously for one hour, it will consume 1 kW h of energy. Thus,
1 kWh is the energy used in one hour at the rate of 1000 Joule per second.