Laws of chemical combination
Law of conservation of mass
According to the law of conservation of mass, mass can neither be created
nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. It can only change its form from one
form to another.
Law of constant proportion
The law of constant proportion is also known as the law of Definite
proportions. It states that in a chemical substance the constituent
elements are always present in definite proportion by mass.
Dalton's Atomic theory
According to this theory element a compound or a mixture consist of small
particles called atoms.
The theory was further explained as
.
Matters are made up of tiny particles called atom.
Atoms are indivisible particles and cannot be created or destroyed.
Atoms of a particular element r identical in mass and chemical property.
Combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compound.
Relative number and kind of atoms R constant in a given compound.
Atom
The smallest particle of matter is an atom. Atoms are the building blocks
of matter. Millions of atoms stacked together to form a thin piece of
paper. The radius of atoms is measured in NM. Since the atom size is very
small we might think that is insignificant, but they are there and also
affecting whatever we do.
Modern day symbols of atom of different elements:
Dalton designed specific symbols for each element in a very specific sense.
Each symbol was meant for a particular element also for a definite quantity
of that element that is a single atom.
Berzelius suggested that the symbol of element can be made from one or two
letters of the name of the elements. nowadays IUPAC (International Union of
Pure and Applied Chemistry) is an international scientific organisation
which approves names for elements symbols and units.
For example: Hydrogen as H, aluminium as Al and Cobalt as Co.
|
Element
|
Symbol
|
Element
|
Symbol
|
Element
|
Symbol
|
|
Aluminium
|
Al
|
Copper
|
Cu
|
Nitrogen
|
N
|
|
Argon
|
Ar
|
Fluorine
|
F
|
Oxygen
|
O
|
|
Barium
|
Ba
|
Gold
|
Au
|
Potassium
|
K
|
|
Boron
|
B
|
Hydrogen
|
H
|
Silicon
|
Si
|
|
Bromine
|
Br
|
Iodine
|
I
|
Silver
|
Ag
|
|
Calcium
|
Ca
|
Iron
|
Fe
|
Sodium
|
Na
|
|
Carbon
|
C
|
Lead
|
Pb
|
Sulphur
|
S
|
|
Chlorine
|
Cl
|
Magnesium
|
Mg
|
Uranium
|
U
|
|
Cobalt
|
Co
|
Neon
|
Ne
|
Zinc
|
Zn
|
Atomic mass
Dalton told in his atomic theory about the atomic mass, each element has a
characteristic atomic mass. Those days determining the mass of an
individual atom was relatively difficult so atomic masses were determined
by using the law of chemical combination and the compounds formed.
Similarly, relative atomic mass of the atom of an element is defined as the
average mass of the atom.
Example: 3 grams of carbon combines with 4 grams of oxygen to form CO.
|
Element
|
Atomic mass
|
|
Hydrogen
|
1
|
|
Carbon
|
12
|
|
Nitrogen
|
14
|
|
Oxygen
|
16
|
|
Sodium
|
23
|
|
Magnesium
|
24
|
|
Sulphur
|
32
|
|
Chlorine
|
35.5
|
|
Calcium
|
40
|
Atoms Existence
Atoms of different element cannot exist independently. A number of atoms
combines together to form molecules or ions. These molecules or ions
aggregates together to form matter which we can see, feel or touch.
Molecules of elements
Molecules of an element are formed by the accumulation of same type of
atoms. molecules of elements like Argon helium are made up of only one atom
of that element. Molecules can be monoatomic, diatomic, polyatomic and so
on. The total number of atoms constituting a molecule is known as its
atomicity.
|
Non-Metal
|
Atomicity
|
|
Argon
|
Monoatomic
|
|
Helium
|
Monoatomic
|
|
Oxygen
|
Diatomic
|
|
Hydrogen
|
Diatomic
|
|
Nitrogen
|
Diatomic
|
|
Chlorine
|
Diatomic
|
|
Phosphorus
|
Tetra-atomic
|
|
Sulphur
|
Poly-atomic
|
Molecules of compounds
When atoms of different elements join together in definite proportion they
form the molecules of a compound. As water molecule consists of hydrogen
and oxygen in the ratio of 1:8.
Ions
Compound composed of metals and nonmetals contains charged species known as
ions. Ions may consist of a single charged atom or a group of atoms that
have a net charge on them. A negatively charged ion is called as "anion"
and a positively charged ion is called as "cation". In the case of (Sodium
Chloride) NaCl, sodium is a positively charged Ion and chloride is a
negatively charged ion.
Writing chemical formulae
The symbolic representation of the composition of a compound is the
chemical formula of that particular compound. The combining power of an
element is known as its valency. With the help of valency, we can
understand that how the atom of a particular element will combine with the
atoms of another element to form a compound.
Formula of simple compounds
Simplest compound made up of only two different elements are called as
binary compounds. For writing the chemical formula of a compound we write
the constituent elements and their valencies and then crossovering the
valency of the combining atoms helps forming the compound.
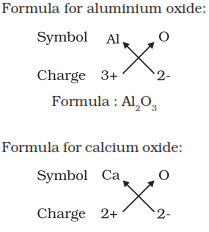
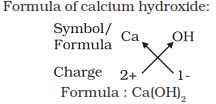
Molecular mass
Molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the
atoms in a molecule of the substance. The relative mass of a molecule is
expressed as atomic mass units(u).

Formula unit mass
Formula unit mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the
atoms in a formula unit of a compound. This calculation is similar to that
of the molecular mass but the only difference is that the substance
constitutes of ion particles.
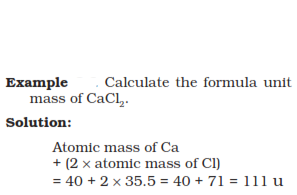
Mole concept
Atoms and molecules are too small to count so the numbers are expressed in
terms of Avogadro number. 1 mole is the number equal to Avogadro's number.
Mole can be defined as a unit which represents 6.023 *1023. mass
of one mole of a substance is called its molar mass.
Example
One mole of carbon atom is equals to 12 grams of carbon atom equals to
6.023*1023 atoms of carbon.
One mole of hydrogen atom is equals to 1 gram of hydrogen atom which is
equals to 6.022*1023 atoms of hydrogen.
Numerical on Mole concept
