When an object is thrown upward after reaching a certain height it starts
falling downward, this happens due to the gravitational force of attraction
of the earth. This was first discovered by newton when he was sitting under
a tree and an apple fell on him.
Universal law of gravitation
Every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force which
is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional
to the square of the distance between them. The force is along the line
joining the center of two objects.
According to the universal law of gravitation the force between two object
is directly proportional to the product of their masses.
G is the constant of proportionality and is called the universal
gravitation constant.
Importance of universal law of gravitation
The force that bind us to the earth.
The motion of the moon around the earth.
The motion of planets around the sun.
The tides due to the moon and the sun.
Free fall
the earth attracts object towards itself this is due to the gravitational
force. Whenever object fall towards the earth under this force alone, we
say that the object is in a free fall. While free fall there is no change
in direction of motion but due to earth's attraction there is a change in
the magnitude of the velocity.
Acceleration due to gravitational force
When an object falls toward the earth and acceleration is involved this
acceleration is due to the earth\ zc's gravitational force and therefore the
acceleration is called the acceleration due to gravitational force of the
earth. It is denoted by g. And the unit of g is metre per second square.
The magnitude of the gravitational force F will be equal to the product of
mass and acceleration due to the gravitational force.
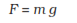
Motion of an object under the influence of gravitational force
Any object during a freefall in absence of any resistance such as air then
the object experiences acceleration and this acceleration experienced by
the object is independent of its mass that is all object hollow or solid,
big or small should fall at the same rate.
G is constant near the earth so, all equations for the uniformly
accelerated motion of object become valid with acceleration a replaced by
g.
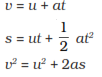
Mass
The mass of an object is the measure of its inertia. The greater the mass
of an object greater is the inertia. The mass of an object remains constant
whether the object is on earth or on moon or even in outer space.
Every object in the earth is attracted towards it with a certain force
depends on the mass of the object and the acceleration due to gravity. The
weight of an object is therefore the force with which it is attracted
toward the earth.
Weight of an object on moon
Weight of an object on the earth is the force with which the earth attracts
the object towards it. In the same way the weight of an object on the moon
is the force with which the moon attracts the object. Since the mass of the
moon is lesser than the mass of earth due to that moon exerts lesser force
of attraction on the object.
Thrust and pressure
the force acting on an object perpendicular to the surface of that object
is called trust. It is the net force applied in a particular direction.
Whereas pressure is the force per unit area acting on the object concerned.
When we stand on sand the area on which the force is applied is less
whereas when we lie down the area of the force being applied increases.
Thus, the effect of force of the same magnitude differ when the surface
areas are different. Pressure can be defined as thrust divided by area.
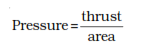
SI unit of pressure is Newton per metre square and it is called as Pascal
denoted by pa.
Pressure in fluid
All liquids and gases are fluid. Solid exerts pressure on the surface due
to its weight similarly fluid have weight and they also exert pressure on
the base and walls of container in which they are enclosed. Pressure
exerted in any confined mass of fluid is transmitted undiminished in all
direction. This is termed as pressure in fluid.
Buoyancy
When an object is floating in a fluid, it is due to the upward force
exerted by the fluid onto the object against the force due to the
gravitational attraction of the earth. This particular force is known as
uptrust or buoyant force. The magnitude of this buoyant force depends on
the density of the fluid.
Object float or sink in water
A cork floats in water while a nail sinks down is because the difference of
the density. The density of a substance is defined as the mass per unit
volume. The density of water is more than the density of cork so it floats
while the density of nail is more than the density of water that's why it
sinks.
Archimedes principle
When a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid it experiences an
upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
Relative density
The density of a substance is defined as mass of a unit volume. Density of
a given substance under a specific condition remains the same. It is often
convenient to express density of a substance in comparison with the density
of water. So relative density can be defined as the density of a substance
divided by the density of water.
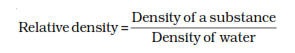
It is a ratio and therefore does not have any unit.