Some natural Phenomena are winds, storms and cyclones are destructive phenomena. In this chapter we will discuss two destructive natural phenomena lightning and earthquakes.
LIGHTNING
- Lightning is an electric spark, but on large scale.
- Lightning is caused by accumulation of charges in the clouds.
- We need to take precautions to protect ourselves from the deadly spark.
- Most of the substances are electrically neutral state. According to basics of atomic structure, an atom is made up of electrons, protons and neutrons.
- An electron has a negative charge, a proton has a positive charge and there is no charge on a neutron.
CHARGING BY RUBBING
- When a plastic comb is rubbed with dry hair it get charged these objects are called charged objects.
- When two objects are rubbed with each other, electrons get transferred from one object to another
- The transfer of charges is responsible for static electricity in various objects.
- Static electricity is the main reason of lightning
TYPES OF CHARGES AND THEIR INTERACTION
Let us see some examples through activities-
Activity 1
- Hang two inflated balloons in such a way that they do not touch each other then, rub both the balloons with a woollen cloth and then release.
- In this activity, we have brought together the charged objects that were made of the same material and rubbed same kind.
- Both the balloons repel each other. So we can conclude that the charges of the same kind repel each other.
Activity 2
- Rub a refill and place it gently in a glass tumbler. Bring an inflated charged balloon (balloon rubbed with a woollen cloth) near the refill.
- The charged balloon attracts a charged refill.
- The charges of different kind attract each other.
TRANSFER OF CHARGE AND EARTHING
ACTIVITY 3
- Let us take an empty jam bottle and a piece of cardboard bigger than the mouth of the bottle.
- Make a hole in cardboard to insert a metal paper clip and Open out paper clip. Now we cut two strips of aluminium foil of dimension 4 cm × 1 cm each.
- Hang them on the paper clip as shown. We insert the paper clip in the cardboard lid perpendicular.
- We charge a refill by rubbing with polythene and touch it with the end of the paper clip. We observe that they repel each other. Now we touch other charged bodies with the end of the paper clip. The foil strips behave in the same way in all cases.(iii) The aluminium foil strips receive the same kind charge from the charged refill through the paper clip (metals are good conductors of electricity) and repel each other and they become wide open.
- Such a device can be used to test whether an object is carrying charge or not. This device is known as
EARTHING
The process of transferring of charge from a charged object to the earth is called earthing.
Earthing is provided in buildings to protect us from electrical shocks due to any leakage of electrical current.
- Electrical charge can be transferred from a charged object to another through a metal conductor. When we touch the end of the paper clip gently with hand, we will find that the foil strips of electroscope come back to their original state.
LIGHTNING
- The transfer of charge from clouds to cloud or from cloud to the earth is called lightning. It is bright streak of light during a thunderstorm with the sound of thunder.
- Lightning is an electric spark which happens on a large scale in the sky by vigorous movement of air currents and the water droplets.
- From these generated charges, the positive charges accumulate at near the upper edges of the clouds and the negative charges accumulate at near the lower edges of the clouds. Scientists are yet to understand the exact reason for this. There is accumulation of positive charges near the ground also.
- When accumulation of charges become very heavy, air is no longer able to resist their flow. As a result, the electric charges transfer to the ground and produce streaks of bright light and sound across the sky. The process is called an electric discharge.

- Dangers-Lightning can damage houses, buildings and trees. It can also kill human life, property and animals.
- Safety:-
First sound of thunder is an alert to rush to a safer place. After hearing the last thunder, we should wait for some time before coming out of the safe place.
- A house or a building is a safe place. During lightning and thunderstorm open place is not safe.
Do’s and Don’ts during a Thunder-storm
- Outside
- Open vehicles, like motorbikes, tractors, construction machinery and open cars are not safe during the lighting.
- Stay away from poles or other metal objects.
- Carrying umbrella is not a good idea at all during thunderstorms.
- In open fields, tall trees, shelters in parks, elevated places do not protect us from lightning strokes. We should take shelter under shorter trees.
- In open area, if you do not find place to hide. Do not lie on the ground. Instead, Place your hands on your knees with your head between the hands. This position will make you the smallest target to be struck.
- Inside
- Lightning can strike telephone cords, electrical wires and metal pipes. During a thunderstorm avoid contact with these.
- Bathing should be avoided during thunderstorms.
- Electrical appliances like computers, TVs, etc., should be unplugged. Electrical lights can remain on. They do not cause any harm.
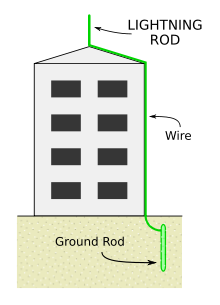
Lightning Conductor- It is a device used to protect buildings from lightning.
- It is a metallic rod, taller than the building, is installed in the walls of the building.
- The base goes very deep inside the earth and one end is kept out in the air.
- When lightning strikes, electric charge goes to the lightning conductor and then it goes to earth. It provides easy route for the transfer of electric charge to the ground.
EARTHQUAKES
- It is a sudden shaking or trembling of the earth, which lasts for a very short period, is called earthquake.
- It is caused by a disturbance deep inside the earth’s crust.
- It can cause large scale destruction and damage to human life.
WHAT CAUSES AN EARTHQUAKE?
- The tremors are caused by the disturbance deep down inside the uppermost layer of the earth called the crust.
- The earth’s crust is made up of several pieces of landmass. These are called tectonic plates. When they brush past one another or a plate goes under another due to collision. They cause vibrations in the earth’s crust. These occur as an earthquake on the surface of the earth.
- Tremors on the earth can also be caused when a volcano erupts, or a meteor hits the earth or an underground nuclear explosion is carried out. However, most earthquakes are caused by the movement of earth’s plates.
SEISMIC ZONE
As earthquakes are caused by the movement of earth’s plates, the boundaries of the plates are the weak zones where earthquakes are more likely to occur. These weak zones are called as Seismic Zone.
RICHTER SCALE
- The power of an earthquake is expressed in terms of a magnitude on a scale called the Richter Scale.
- Very destructive earthquakes have magnitudes higher than 7 on the Richter scale.
- The Richter Scale was developed in 1935 by Charles Richter and Beno Gutenberg of California Institute of Technology
- Richter scale is not linear. This means an increase of 2 is magnitude means 1000 times more destructive energy.
- Example: an earthquake of magnitude 6 has thousand times more destructive energy than an earthquake of magnitude 4.
PROTECTION AGAINST EARTHQUAKE
Earthquakes cannot be predicted & they cause destruction. Therefore, it is important to take necessary precautions to protect ourselves in time.
- Buildings in the seismic zones should be designed ‘quake-safe’.
- Consult qualified architects & structural engineers.
- In highly seismic areas, the use of mud or timber is better than using heavy construction material.
- Roof should be as light as possible, so that if the structure falls, the damage will not be heavy.
- Cupboards & shelves should be fixed on the walls, so that they do not fall easily.
- Since some buildings may catch fire due to an earthquake, it is necessary that all buildings have fire fighting equipment in working order.
PROTECTION DURING A AN EARTHQUAKE
- The buildings should be designed so that they can withstand major tremors.
- The use of mud or timber is better than the heavy construction materials for making the buildings in earthquake prone areas.
- Cupboards and shelves should be fixed to the walls so that they do not fall on someone during an earthquake.
When Earthquake strikes, following steps should be taken to protect self:
INDOORS
- Take shelter under a table & stay there till the shaking stops.
- Stay away from tall & heavy objects.
- If you are in bed, do not get up. Protect your head with a pillow.
OUTDOORS
- Find a clear spot, away from buildings, trees & overhead power lines. Drop to the ground.
- If you are in a car or a bus, do not come out. Ask the driver to drive slowly to a clear spot. Do not come out till the tremors stop.