A) INTRODUCTION
We all know that every living organism needs food to survive. Plants can
synthesise their own food but, animals including human beings are dependent
on others for food. So for providing food for large number of people we
need proper management.
So for this large scale demand of food for humans, they started agriculture
practises.
AGRICULTURE - it is a human activity of cultivating crops and
plantations for the large scale production of food and goods such as bio
fuels, fibres, animal feed etc.
CROPS- when the plants of same types are cultivated at a place on a very
large scale are known as crop.
B) TYPES OF CROPS IN INDIA
India is a vast country where diverse practices of farming are seen in
different parts. But crops in India can be divided into two main types,
which are basically:
-
Kharif
(monsoon crops) - these are sown in the beginning of rainy season.
Ex-paddy, maize, cotton etc.
-
Rabi
(winter crops) - these are sown in the beginning of winter season.
Ex-wheat ,gram, pea etc.
Besides these kharif and Rabi season ,pulses and vegetables are also grown in summer season.
C) BASIC PRACTICES OF CROP PRODUCTION
Cultivation of crop involves various activities and steps which are
referred as agriculture practices. There are seven agriculture practices.
These activities are-
1) Preparation of soil
2) Sowing
3) Adding manure and fertilisers
4) Irrigation
5) Protection from weeds
6) Harvesting
7) Storage
Let us see each point in detail.
c.1)
PREPARATION OF SOIL
One of the most important steps in preparation of soil is to loosen it,
which allows the microorganism and earthworm to enrich the soil. This helps
the root to penetrate deep into the soil and also bring the nutrient rich
soil on the top layer.
The process of loosening or turning of soil is called tilling or ploughing.
PLOUGHING
-
This is done with the help of plough.
-
Ploughed field contains big pieces of soil called crumbs.
· Further it is levelled using a wooden or an iron leveller to prevent
the soil from being eroded by wind or water.
· Next manure or fertilizer is added to increase the soil fertility.
Plough
-
it is tool for ploughing in olden days.
-
Made up of wood or iron.
-
It contains triangular iron strip called as the ploughshare.
-
The main part is a rod of wood known as plough shaft.
· The last end is attached to the beam which is attached to the bull.
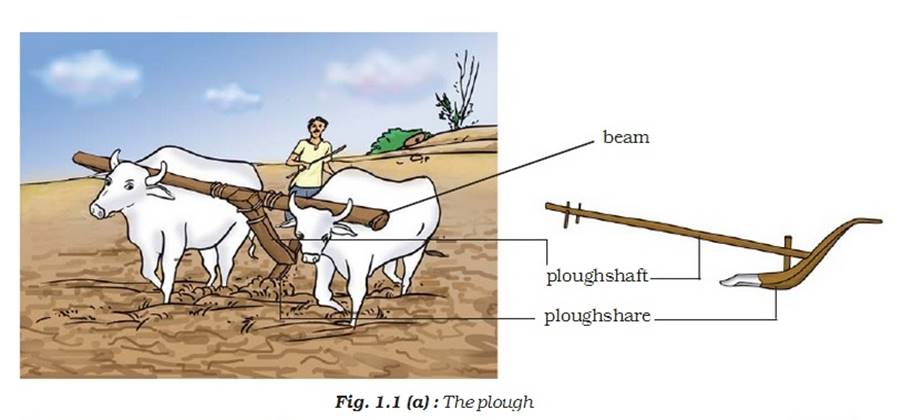
H
oe
-
It helps in removing the weeds.
-
It has long rod made up of wood or iron.
-
A strong bent plate made up of iron is present at one end.
-
This is pulled generally by ox.
Cultivator
Cultivator:
Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor driven cultivator. The use of
cultivator saves labour and time. [Fig.1.1 (c)]

c.2) SOWING
· Seeds which are used for sowing should be of good quality, healthy
and free from infections.
-
Seeds must be planted at correct depth in the soil.
-
Proper amount of water is needed for the seeds to germinate.
· The gap between the seeds should be proper and at the right
distance.
Traditional tool
-
it is shaped like a funnel
-
Funnel's end is pierces into the soil.
-
Funnel is passes through the funnel
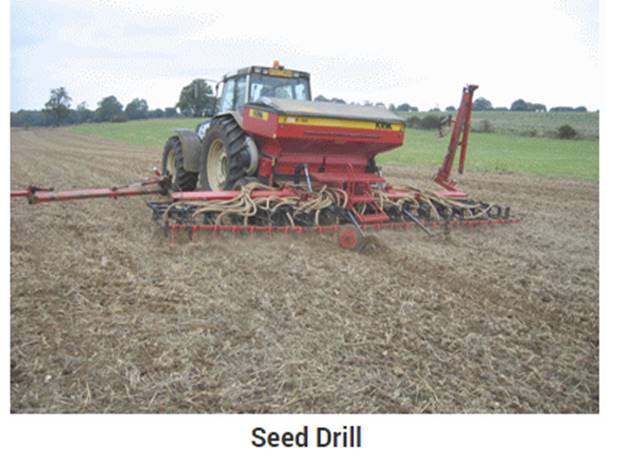
Seed drill
-
Now days drills are used present in the tractors.
-
It sows the seeds uniformly at proper distance and depth.
-
It ensures that seeds are properly covered by the soil.

c.3) ADDING MANURE AND FERTILIZERS
· Soil itself supplies necessary minerals and nutrients to the plant.
· In certain areas when farmer grows crops after crops it decrease the
fertility of the soil.
HOW TO INCREASE SOIL FERTILITY
- Nutrients are added for healthy growth of plants is called manure and fertilizers.
- To improve the fertility farmers use to add manure to the soil called manuring.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MANURE AND FERTILIZERS
|
S.no.
|
Manure
|
Fertilizers
|
|
1.
|
Made up of animal and plants waste
|
Made up of chemicals in factories
|
|
2.
|
Provides mainly organic matter
|
Provides mainly nutrients
|
|
3.
|
No side effects as it is natural
|
Gives side effects
|
|
4.
|
Provides long term soil fertility
|
Not good for long term soil fertility
|
|
5.
|
It is cheaper
|
It is costlier than manures
|
|
6.
|
It gives slow result
|
Provides fast and effective result
|
c.4) IRRIGATION
Supply of water to crops at different interval of time is known as
IRRIGATION
· Water is the basic and important requirement for growth and
development of plants.
· Germination of seeds doesn't take place under dry conditions.
· Proper irrigation system will ensure the timely and adequate
required water to crops. This will lead to more yield.
Sources of irrigation
: wells, tube wells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canals.
1.
Traditional method of irrigation:
The water available in wells, lakes and canals is lifted up by different
regions, for taking it to the fields.
Various traditional methods are:-
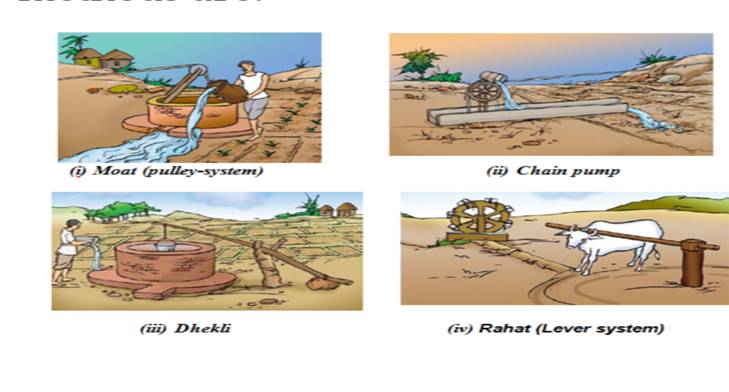
2.
Modern methods of irrigation:
a.
Sprinkler system:
· Used where uneven land is present.
· Perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top.
· Joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals.
· Water is flowed under pressure with the help of pump, escaping
through rotating nozzles and gets sprinkled.

b.
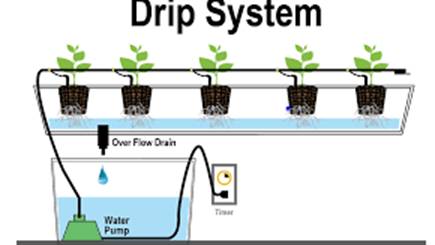
Drip system:
· Water falls drop by drop at the position of the roots.
· Best technique for watering fruit plants, garden and trees.
· Very less water wastage.
C.5) PROTECTION FROM WEED
Weeds
are the undesirable plants which grow naturally along with the crops.
· Removal of weeds is called weeding.
· Weeding is important as they effect the growth of crop by compete
with the crop plants.
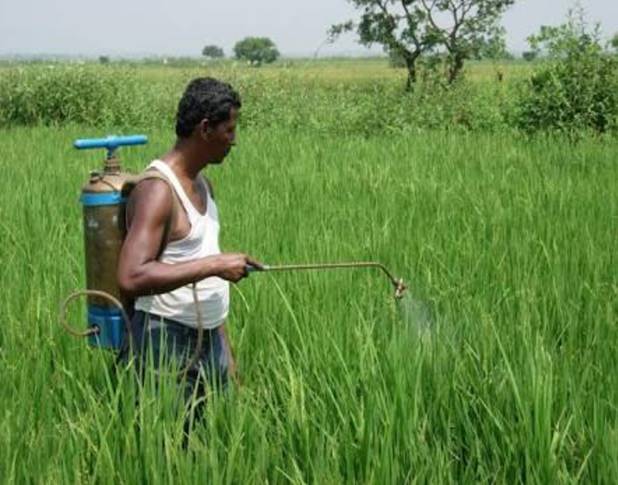
WEED CONTROL
· Tilling before sowing of crops helps in uprooting and killing of
weeds.
· Manual removal includes physical removal of weeds by cutting them.
· Weeds are control by spraying weedicides.
· Weedicides are the chemical to kill the weed.

C.6
) HARVESTING
Cutting of crops after it is mature is called harvesting.
· Crops are pulled out or cut close to the ground.
· It can be done manually by sickle or by machine.
· The grain seed need to be separated from the chaff with the help of
machine called "combined".

C.7) STORAGE
· Grains are kept for the longer time without getting spoiled is known
as storage.
· Should be kept safe from moisture, insect, rats and microorganisms.
· If grains are stored without drying they may get spoilt and lose
their germination capacity.
· Small scale storage in jute bags and metallic bins.
· Large scale storage in silos and granaries.
D) FOOD FROM ANIMALS
· Like plants, animals also provide us with different kinds of foods.
· People living in coastal areas consume fish as a major part of their
diet.
· Just like crop production involve number of steps ,similarly animals
reared at home or in farm
· When this is done on large scale it is known as animal husbandry.