Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce more
living organisms of its own kind.
MODES OF REPRODUCTION
There are two modes by which animals reproduce.
1. Asexual Reduction:
The process of reproduction in which new individuals are produced from a
single parent. E.g. - microorganisms.
2.
Sexual Reproduction:
The process of reproduction in which two individuals are involved to
produce a new individual. E.g. Human, tiger
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
-
In animals, males and females have different reproductive parts or
organs.
-
The reproductive parts in animals produce gametes that fuse to form a
zygote. It is the zygote which develops into a new individual.
-
This type of reproduction beginning from the fusion of male and female
gametes is called sexual reproduction.
REPRODUCTIVE ORGAN IN HUMANS
1. Male Reproductive Organs
-
Reproductive organs - A pair of testes (singular, testis), two sperm
ducts and a penis.
-
The testes produce the male gametes called sperms.
-
Though sperms are very small in size, each has a head, a middle piece and
a tail.
-
It is a single cell with all the usual cell components.
Female Reproductive Organs
-
A pair of ovaries, oviducts (Fallopian tubes) and the uterus.
-
Ovary produces female gametes called ova (eggs).
-
In human beings, a single matured egg is released by one of the ovaries,
into the oviduct every month.
-
An egg is also a single cell.
FERTILIZATION
The process of fertilization is fusion of a male gamete (Sperm) with a
female gamete (Ovum) is called fertilization. Zygote is formed after
fertilization.
TYPES OF FERTILIZATION
There are two types of fertilization in animals, external fertilization and
internal fertilization.
-
Internal Fertilisation:
When fertilization takes place inside the animal's body, it is called
internal fertilization. Internal fertilization occurs in animals,
humans, cows, dogs and hens.
-
External Fertilisation:
In this fertilization, the fusion of a male and a female gamete takes
place outside the body of the animal's body. It is very common in
aquatic animals such as fish, starfish, etc.
Example: During spring or rainy season, frogs and toads move to ponds
and river. When the male and female come together in water, the female
lays the eggs, the male deposits sperms over them. Each sperm swims
randomly in water. The sperms then come in contact with the eggs.
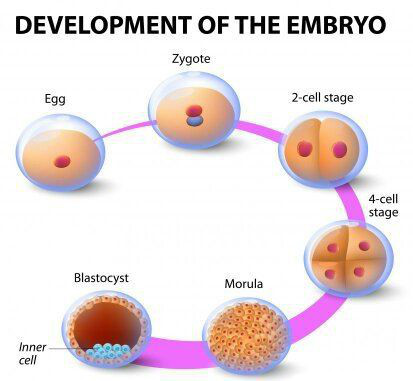
DEVELOPMENT OF EMBRYO
Development of embryo takes place in the female reproductive system through
following steps:
-
Every month, a single egg comes out of the ovary and reaches the
fallopian tube of female reproductive system.
-
During copulation, sperms reach the Fallopian tube where a sperm
fertilizes the egg results in formation of zygote.
-
The zygote divides repeatedly .The cells then begin to form groups that
develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing
structure is known as embryo.
-
The embryo gets implanted in the wall of the uterus for further developed
the body parts such as hands, legs, head, eyes, etc.
-
The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts can be identified is
called as foetus.
-
When the development of the foetus is complete, the mother gives birth to
the baby.
Internal fertilization takes place in hens also-
Formation of Egg Shell in Hens
After fertilization, the zygote divides continuously and moves to the oviduct. As it travels down, many protective layers are formed around it. The hard shell in a hen's egg is one such protective layer. After the hard shell is formed, the finally hen lays the egg. The embryo takes about 3 weeks to develop into a chick. After the chick is completely developed it bursts open the egg shell.
VIVIPAROUS ANIMALS
The animals which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals.
Examples- Human being, dog, cows.
OVIPAROUS ANIMALS
-
Those animals which lay eggs are called oviparous animals. Examples -
hen, frog etc.
YOUNG ONES TO ADULTS
1.
When the young ones of an animal resemble the adult, then direct
development takes place, e.g. hen, man, monkey, etc.
2.
When the young ones of an animal do not resemble the adult, then indirect
development takes place, e.g. frog, butterfly, silk moth, etc.
3.
Metamorphosis
: In case of indirect development, transformation of young ones into adult
through drastic changes is called metamorphosis. Example- Larva of
butterfly . A tadpole into frog.
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION METHODS
Reproduction in which only single parent is involved is known as asexual
reproduction. Example - microorganism like amoeba, hydra etc.
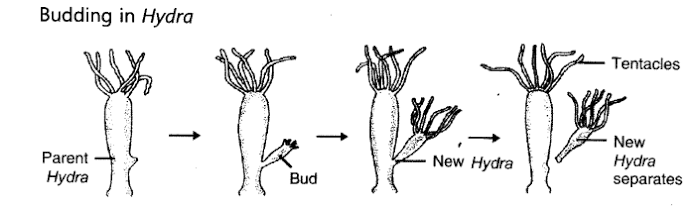
1.
Budding
:
This reproduction method is seen in those multi cellular animals which are
highly simple in structure. A small bud develops on the body. After
developing the bud, it gets detached from the parent's body as a new
individual. Since new individuals develop from the buds, this type of
asexual reproduction is called budding. Examples: Hydra
and sponges.
2. Binary Fission:
This reproduction is seen in unicellular animals, example- amoeba. In this
an organism divides into two daughter cells. First the nucleus divides and
forms two daughter nuclei. Then the cytoplasm in the mother cell divides
into two daughter cells. This leads to the formation of the two daughter
cells each having a nucleus and its own cell organelles which then develop
into a fully formed adult.
Example - paramecium, leishmania etc.
Cloning
Cloning is process of production of an exact copy of a cell, any other living part, or a complete organism. Cloning process of an animal was successfully performed for the first time by Ian Wilmut and his colleagues at the Roslin Institute in Edinburgh, Scotland. They cloned successfully a sheep named Dolly.