WHAT IS COMBUSTION?
Combustion:
It is a chemical process in which a substance reacts with the oxygen to
give off heat is called combustion.

Any material pr substance that undergoes combustion is known ascombustible substance. It is also called as fuel.
Examples - petrol, diesel, etc.
The fuel may be in solid, liquid or gas state. Sometimes, light is also
given off during combustion, either as a flame or as a glow.
Ignition Temperature: minimum temperature at which any
material catches fire is known as ignition temperature.
Example-
-
If the temperature of combustible substance is lower than the ignition
temperature then the substance will not burn.
-
Cooking oil catching fire when a frying pan is kept for long on a
burning stove.
-
Kerosene oil and wood do not catches fire their own at room temperature.
But, if kerosene oil is heated a little, it will catch fire. But if wood is
heated a little, it would still not catch fire.
Matchsticks
Since ages, matchsticks are in use. Long ago, Egyptians used small pieces of pinewood dipped in sulphur as matches. These days matchsticks are lot safer.
Modern matchsticks are made up with mixture of antimony trisulphide and potassium chlorate with some glue and starch applied on the head of the match. The rubbing surface has powdered glass and some red phosphorous. On striking match against rough surface, red phosphorous gets converted into white phosphorous and it reacts with potassium chlorate to ignite antimony trisulphate and so the combustion takes place
Inflammable Substances
Those materials which have low ignition temperature and catch fire easily
are termed as inflammable substances.
Example - petrol, LPG, alcohol etc.
THREE ESSENTIAL REQUIREMENTS FOR PRODUCING FIRE
-
Fuel
-
Air (With Oxygen in it).
-
Temperature above the Ignition temperature.
HOW DO WE COTROL FIRE?
1. Fire Brigade Stations
In case of fire, fire brigades will extinguish the fire by sprinkling the
water on the affected areas. The water will bring down the temperature
below its ignition temperature. As a result, fire will stop spreading.
2. Fire Extinguisher
Water is the most common fire extinguisher. But, it works only on things
like wood, paper, etc. However, in case fire is caught on electrical things
then, water being good conductor of electricity will destroy that
equipment. Even water is not good in case of fires due to oil, petrol, etc.
in that cases, Carbon dioxide is best extinguisher. This cut off the air
supply and t brings down the temperature below the ignition temperature as
a result fire gets extinguished.
3.
Use of Blankets
if a person catches the fire, then blankets can be used to extinguish the
fire.
4. Forest Fires
when temperature rises too high then the regions having dry grasses will
catch the fire. This fire spreads rapidly from grasses to trees and
eventually entire forest is on fire. And it is difficult to manage such
fires.

TYPE OF COMBUSTION
1. Rapid Combustion
In this combustion, the substances burns rapidly and produces light and
heat.
Example: Bring a burning matchstick near a gas stove in the kitchen. Turn
on the knob of the gas stove. We find that the gas burns rapidly.
2. Spontaneous Combustion
In this type of combustion, substances burst out into flames suddenly
without any known reason.
Examples: Many disastrous fires in coal mines result due to this kind of
combustion. The heat rays coming from the sun or a lightning strike might
be responsible for this kind of combustion.
3. Explosion
In this type of combustion, all of a sudden reaction results into heat,
light and sound. Moreover, large amount of gas gets released.
Example: When a fire cracker is ignited, a sudden reaction takes place with
the evolution of heat, light and sound with the large amount of gas.
Flame
The substances which vaporise while burning, give flames. It is a place
where combustion of fuel takes place.
Kerosene oil
and molten wax are substances that give a flame while
burning. This gas is called as flame.
Flame structure
When flames are observed carefully, one can notice different layers of
flame as shown in figure below:
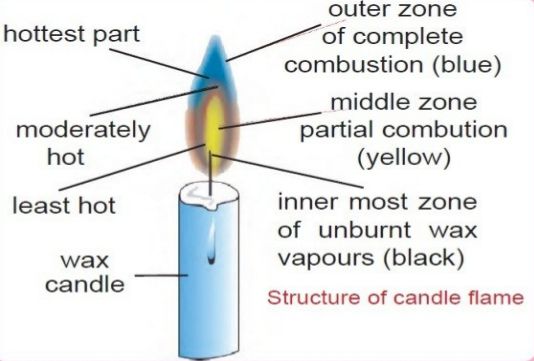
Outermost zone
:
It is blue in colour and is hottest amongst all the zones. In this portion,
complete combustion takes place.
Middle zone:
It is yellow in colour and is somewhat hot. In this portion, partial
combustion takes place.
Innermost zone:
It is black in colour and is coolest amongst all the zones.
FUEL
The substance that undergoes combustion is known as fuel. Examples of fuels
are charcoal, petrol, kerosene, wood, etc.
Characteristics of good fuel
-
It should be easily available and cheap.
-
It should generate large amount of heat.
-
It should not leave any unwanted matter after combustion.
Ideal Fuel
The fuel which satisfies all the characteristics of good fuel is termed as
an ideal fuel. But probably, there is no fuel considered as an ideal fuel.
Fuel Efficiency
-
The quantity of heat generated on combustion of 1 kg of a fuel is called
its calorific value.
-
Its unit is kilojoules per kg (KJ/kg).
Calorific Values of Different Fuels
|
Fuel
|
Calorific Value(kJ/kg)
|
|
Cow dung cake
|
6000 - 8000
|
|
Wood
|
17000 - 22000
|
|
Coal
|
25000 - 33000
|
|
Petrol
|
45000
|
|
Kerosene
|
45000
|
|
Diesel
|
45000
|
|
Methane
|
50000
|
|
CNG
|
50000
|
|
LPG
|
55000
|
|
Biogas
|
35000 - 40000
|
|
Hydrogen
|
150000
|
HARMFUL EFFECT OF BURNING FUEL
The increasing fuel consumption has harmful effects on the environment.
-
Carbon fuels cause many respiratory diseases. It release unburnt carbon
particles.
-
The partial burning of some fuels releases carbon monoxide, which is a
poisonous gas. And this gas can kill a person if left in a room filled with
this gas.
-
GLOBAL WARMING-
Combustion of most fuels the increase the amount of carbon dioxide in
the atmosphere that has lead to increase in the average temperature on
the earth.
-
ACID RAIN-
Due to burning of coal and diesel, Chemicals like sulphur dioxide and
nitrogen dioxide are released into the air. The pollutants reacts with
the water vapour present in the air and forms sulphuric and nitric
acid. When it rains, these acids are also present. Such kind of rain is
called Acid Rain. It is very harmful for crops, buildings and soil.
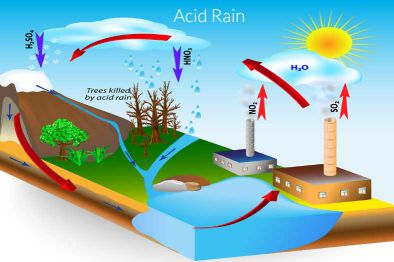
Prevention from Acid rain
:
The use of diesel and petrol as fuels in automobiles is being replaced by
CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), because CNG produces the harmful products in
very small amounts. CNG is a cleaner fuel.