- The changes in the type of natural vegetation occur mainly because of the changes of climatic condition.
- The temperature in an area or a region depends on its height. A place is usually colder if it is higher from the sea level. Temperature of an area affects the type of natural vegetation in that region.
- The type of vegetation that grows in a region also depends on the moisture, slope of land, and thickness of soil. Depending on these factors, vegetation is divided into three categories
- Forests
Forests are huge groups of trees and plants that grow in regions with medium to hot temperatures and plentiful rains.
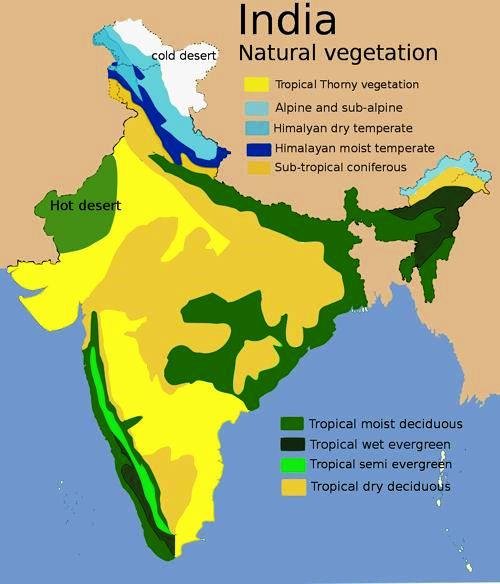
- Tropical Evergreen Forests
- are also known as rainforests and occur in regions near the equator and the tropics
- receive a heavy rainfall throughout the year
- don't shed their leaves ever due to the absence of a particular dry season and this is the reason they are called evergreen
- The tress in these rainforests grow close to each other and have thick tree cover at the top (canopies) which do not allow sunlight to reach the ground even in the daytime.
- Important trees in rainforests are rosewood, mahogany and ebony. These trees are also called hardwood trees.
- Anaconda, one of the world’s largest snakes, is found in the tropical rainforest.
- In India, evergreen forests are found in the deltas of Ganga, Godavari, Mahanadi, Yamuna and other rivers. They can also be found in northern Andaman and Nicobar, Tamil Nadu coast, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, upper parts of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Tripura and West Bengal.
- Tropical Deciduous Forests
- are also called monsoon forests and are found in India, northern Australia, and Central America
- The trees here experience seasonal changes and shed their leaves in the dry season to save water.
- Hardwood trees found here are sal, teak, neem, and sheesham. These trees are very useful in making furniture, transportation and construction materials.
- Animals found in those forests are lions, tigers, monkeys, elephants, and langurs.
- In India, Tropical deciduous forests are found throughout the northern part of India except in the Northeast. These forests can also be found in eastern slopes of Western Ghats, Chhattisgarh, Orissa, Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- Temperate Evergreen Forests
- are located in the mid-latitudinal coastal regions and, mostly in the eastern margins of continents
- are commonly found in south east USA, South China and South East Brazil
- comprise of both hard and soft wood trees like oak, pine and eucalyptus
- The tropical evergreen forest in Brazil is so enormous that it is like the lungs of the earth as the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed and the amount of oxygen released by this forest is immense.
- Temperate Deciduous Forests
- are found in higher latitudinal regions like the north-east of the USA, New Zealand, China, and Chile
- can also be found in the coastal regions of Western Europe
- shed their leaves in the dry seasons
- Common trees found here are oak, ash, beech etc.
- Deer, wolves, fox are the common animals and the pheasant and the monal are common birds.
- Deciduous forests are of two major categories
- The moist deciduous forests
- are found in Shiwalik foothills, Bhabar, Tarai, the North-eastern Deccan Plateau, Chota Nagpur Plateau and North-south strip to the east of the Western Ghats
- Teak is an example of trees found in these forests.
- The dry deciduous forests
- are found in the Central India where rainfall is comparatively less
- Sal is an example of trees found in these forests.
- Mediterranean Vegetation
- The west and south west margins of the continents have Mediterranean vegetation
- This type of vegetation gets its name from the Mediterranean Sea bordering Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- It is also found in California in the USA, South West Africa, South West of South America and South West Australia, regions that are marked with hot dry summers and mild rainy winters.
- Cultivation of citrus fruits such as oranges, figs, olives and grapes takes place in areas with Mediterranean vegetation. Due to this reason Mediterranean regions are also known as ‘Orchards of the world’.
- Not much of wildlife is found here.
- Their thick barks and wax coated leaves help Mediterranean trees to reduce transpiration and thus adapt themselves to dry summers.
- Coniferous Forests
- They are found in the higher latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere, such as in the Himalayas, and are also known as the taiga (meaning pure or untouched in Russian language).
- They have softwood evergreen trees such as chir, pine, deodar cedar that are used to make pulp for the paper and box-making industries.
- Animals like the silver fox, the mink, and the polar bear are found here.
- Grasslands
They grow in regions of moderate rainfall.
- Tropical Grasslands
- They grow on both sides of the Equator and extend to the tropics.
- They grow in regions of moderate to low rainfall areas.
- Grass in this region grows up to 3-4 metres high, and the Savannah grasslands of Africa are of this type.
- Elephants, zebras, giraffes, deer, leopards, etc. are animals found in this region.
- Temperate Grasslands
- They are found in mid-latitudinal regions and interior parts of countries, and the grass there is short and nutritious.
- Wild buffaloes, bisons and antelopes are the common animals found in these regions.
- Thorny bushes
- These are found in the dry desert like regions.
- Tropical deserts are located on the western margins of the continents.
- The vegetation cover is scarce here because of scanty rain and scorching heat.
- Shrubs
- are found in the desert regions in the west of most continents and are scarce because of scanty rains and scorching heat
- are very scarce in the Polar Regions as the climate is very cold
- Only mosses, lichens and very small shrubs are found in the Polar Regions, and this type of vegetation is called tundra which grows during the very short summers when it's not very cold.
- The tundra type of biome is found in the northern parts of Europe, Asia, and North America.
- Animals there have thick fur and skin to protect them from the extreme cold, and the ones commonly found there are seals, walruses, musk oxen, polar bears, snow foxes, Arctic owls etc.
Take a test on this Chapter
Now, you have read the notes on this chapter, take a test to check your understanding of this chapter.
Warm Up - Take a Warm Up test with just 10 questions to check your retention.
Prepare - Deeper check of your Knowledge, take this test of 25 questions.
Buy Whole package. It will have all the chapters of all the Subjects.